How do Fibre Optic Cables Transmit Data?
Nowadays, almost all internet providers deliver internet to your house through fibre optic cables instead of satellite or copper connections. Fibre optic cable transmits data using light instead of an electrical current. It has several advantages over the old internet transmission technology, so more and more consumers are opting for services such as the National Broadband Network (NBN).
While most people are aware that an optical fibre delivers a faster, more reliable internet service, they may not know how fibre optic technology works. Therefore, we will explain how fibre optic cable transmits data. But first, let’s explore what optical fibre is.
What is Optical Fibre?
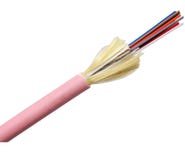
A fibre optic or optical fibre is a thin strand of glass through which information gets transmitted as light pulses. Fibre optics as a transmission medium is capable of carrying signals at very high speeds over long distances, making it superior to traditional copper networks.
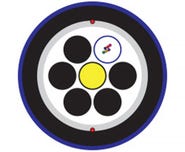
A fibre optic cable can contain a number of glass fibres. The glass strand carrying the data has an outer glass layer with a different refractive index, which keeps the light travelling through the core of the fibre. This allows signals to travel long distances with very minimal attenuation (loss).
Main parts of an optical fibre
An optical fibre is a transmission medium that has three main parts, including the outer jacket/coating, cladding, and core.
The core is the most crucial part of an optical fibre cable and is made up of special glass with a very low refractive index.
Another glass layer surrounds the core, known as the cladding. The cladding reflects light and allows the light beam to travel down the core and reach the receiver with minimal loss. So, an optical fibre relies on the total internal reflection phenomenon to transmit data.
Finally, the core and the cladding are wrapped in an outer jacket/coating to protect it from damage. The outer coating also helps to absorb shock and gives extra protection to the optical fibre.
Now let's move into the final section of this article, where we will reveal how an optical fibre cable transmits data.
How do optical fibre cables transmit data?
Data is transmitted as light instead of power as used in copper cable. However, just like traditional power-based networks, the data is in the form of bits and bytes of information or essentially binary code. It does this faster and more reliably than copper cables due to the speed at which light travels. Additionally, fibre optic cables are designed to minimise attenuation and eliminate interference from outside power sources. The added benefit is security, as light is not as susceptible as power to malicious interference e.g. hacking.
Conclusion
There are many advantages to running fibre optic networks versus traditional copper networks. You should now have a basic understanding of what a fibre optic cable is, how it is constructed, and how data is transmitted via light using fibre optic technology. Fibre networks deliver a fast, secure and reliable internet service.
Recent Articles

Test Network Cabling & Patch Cords FAST with the New DATATESTER by CABAC
Testing LAN cables is quick and easy when you’ve got the new CABAC DATATESTER on hand. This budget LAN cable tester is perfect for contractors who need to test data and coaxial cable for correct termination.
View Products
Exploring the Advantages of Thin Patch Leads
For Australian data installers, selecting the right network components is critical to achieving the performance and reliability that your customers expect. Among these components, the humble patch lead plays a crucial role in interconnecting various devices.
View Products
FOBOT Buying Guide
In this informative article, we will provide a basic buying guide for FOBOTs or “Fibre Optic Break Out Trays” so that you can choose the right product for your specific needs.
View Products
What is a FOBOT?
In this article, we will explain what a FOBOT is and where they are used. We will also describe how a FOBOT works and the important role this component plays in managing and distributing optical fibres efficiently. So, if you're looking to learn all about FOBOTs, make sure to read this article...
View Products
What is the difference between OS1 and OS2 Singlemode Optical Fibre?
This technical article delves into the differences between OS1 and OS2 Singlemode fibre optics, including their core characteristics, performance specifications, and ideal applications.
View Products