What is a fibre optic cable? What is the difference between fibre optic cables and Ethernet cables?
In this day and age, the Internet has become fundamental for communicating information and working efficiently. The accessibility of sufficient high-speed Internet can have a serious influence on productivity. With the exception of wireless networks, there are two principal approaches for transmitting data to a business or home: Ethernet cables transmitting data by electrical impulses and fibre-optic cables transmitting data via light.
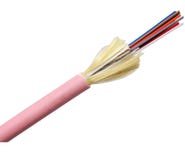
What is a fibre optic cable?
Fibre-optic cable has become progressively more prevalent as the necessity for faster data transmission speed in networks has grown. While fibre-optic cables are a modern way of connecting homes and businesses to the internet, the principle was first used medically between 1890-1910 and later proven for data uses in the 1960s.
A fibre-optic cable performs the same function as an Ethernet cable but is used to transmit light instead of electricity. Fibre-optic cables utilise light pulses to deliver effective long-distance communication and high-speed information transmission. Fibre-optic cables can typically carry data at speeds of 10 Gbps, 40 Gbps, and even 100 Gbps. As a basis, it is widely implemented in Internet, cable and satellite, and telephone systems around the globe.
How does fibre optic cable work?
Data is sent through a fibre-optic cable in the form of light particles termed photons. The refractive index of the core and cladding differs significantly, keeping the light being transmitted in the core of the cable.
Due to the general principles of light travelling through glass, the light signals do not pass at the speed of light but instead at a rate that is approximately 30% slower.
What is the difference between fibre optic cables and Ethernet cables?
| Sl No. | Point of Difference | Fibre optic cable | Ethernet cable |
| 1 | Construction | A fibre-optic cable is constructed of small glass or plastic fibres contained in loose tubes or tight-buffered within an outer sheath. Cable construction can vary. | Copper strands are utilised in Ethernet cables. These are constructed in four pair groupings. This is known as a balanced cabling system. |
| 2 | Cost | Fibre-optic cables tend to be more expensive than ethernet cables. | Fibre-optic cables tend to be more expensive than ethernet cables. Ethernet cables are more readily available and more cost effective. |
| 3 | Speed of transmission offered | Standard fibre-optic lines transmit data at speeds spanning from 1 Gbps to 10 Gbps. However, a single strand of the fibre-optic cable has been demonstrated to carry data at speeds of up to 100 Gbps. | Standard Ethernet cables transmit data at speeds from 1 Gbps to 10 Gbps but changes in encoding practices allow transmission of data up-to 40 Gbps over short distances. |
| 4 | Mode of transmission of data | Fibre optic cables sends information using beams of light rather than electrical currents, which is considerably speedier. | Electrical impulses are utilised to transmit data through Ethernet cables. |
The contrasts between fibre-optic and ethernet cables are considerable, and while fibre-optic cables are projected to become more ubiquitous in terms of mainstream technology standards in the foreseeable future, ethernet cables are still expected to feature prominently for the time being.
Recent Articles

Test Network Cabling & Patch Cords FAST with the New DATATESTER by CABAC
Testing LAN cables is quick and easy when you’ve got the new CABAC DATATESTER on hand. This budget LAN cable tester is perfect for contractors who need to test data and coaxial cable for correct termination.
View Products
Exploring the Advantages of Thin Patch Leads
For Australian data installers, selecting the right network components is critical to achieving the performance and reliability that your customers expect. Among these components, the humble patch lead plays a crucial role in interconnecting various devices.
View Products
FOBOT Buying Guide
In this informative article, we will provide a basic buying guide for FOBOTs or “Fibre Optic Break Out Trays” so that you can choose the right product for your specific needs.
View Products
What is a FOBOT?
In this article, we will explain what a FOBOT is and where they are used. We will also describe how a FOBOT works and the important role this component plays in managing and distributing optical fibres efficiently. So, if you're looking to learn all about FOBOTs, make sure to read this article...
View Products
What is the difference between OS1 and OS2 Singlemode Optical Fibre?
This technical article delves into the differences between OS1 and OS2 Singlemode fibre optics, including their core characteristics, performance specifications, and ideal applications.
View Products